Array
- An array is a collection of similar data elements. These data elements have the same data type. The elements of the array are stored in consecutive memory locations and are referenced by an index.
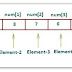
- In C, arrays are declared using the following syntax:
- int a[10];
- The above statement declares an array ‘a’ that contains 10 elements. In C, the array index starts from zero. This means that the array ‘a’ will contain 10 elements in all.
|
1st
Element
|
2nd
Element
|
3rd
Element
|
4th
Element
|
5th
Element
|
6th
Element
|
7th
Element
|
8th
Element
|
9th
Element
|
10th
Element
|
|
a[0]
|
a[1]
|
a[2]
|
a[3]
|
a[4]
|
a[5]
|
a[6]
|
a[7]
|
a[8]
|
a[9]
|
Limitations
of Array
- Arrays are of fixed size.
- Data elements are stored in contiguous memory locations which may not be always available.
- Insertion and deletion of elements can be problematic because of shifting of elements from their positions.
Applications
of Arrays
- Arrays are widely used to implement mathematical vectors, matrices, and other kinds of rectangular tables.
- Many databases include one-dimensional arrays whose elements are records.
- Arrays are also used to implement other data structures such as strings, stacks, queues, heaps, and hash tables.
- Arrays can be used for sorting elements in ascending or descending order.
 08:08
08:08






No comments
Post a Comment